By MARCIA DUNN | Associated Press
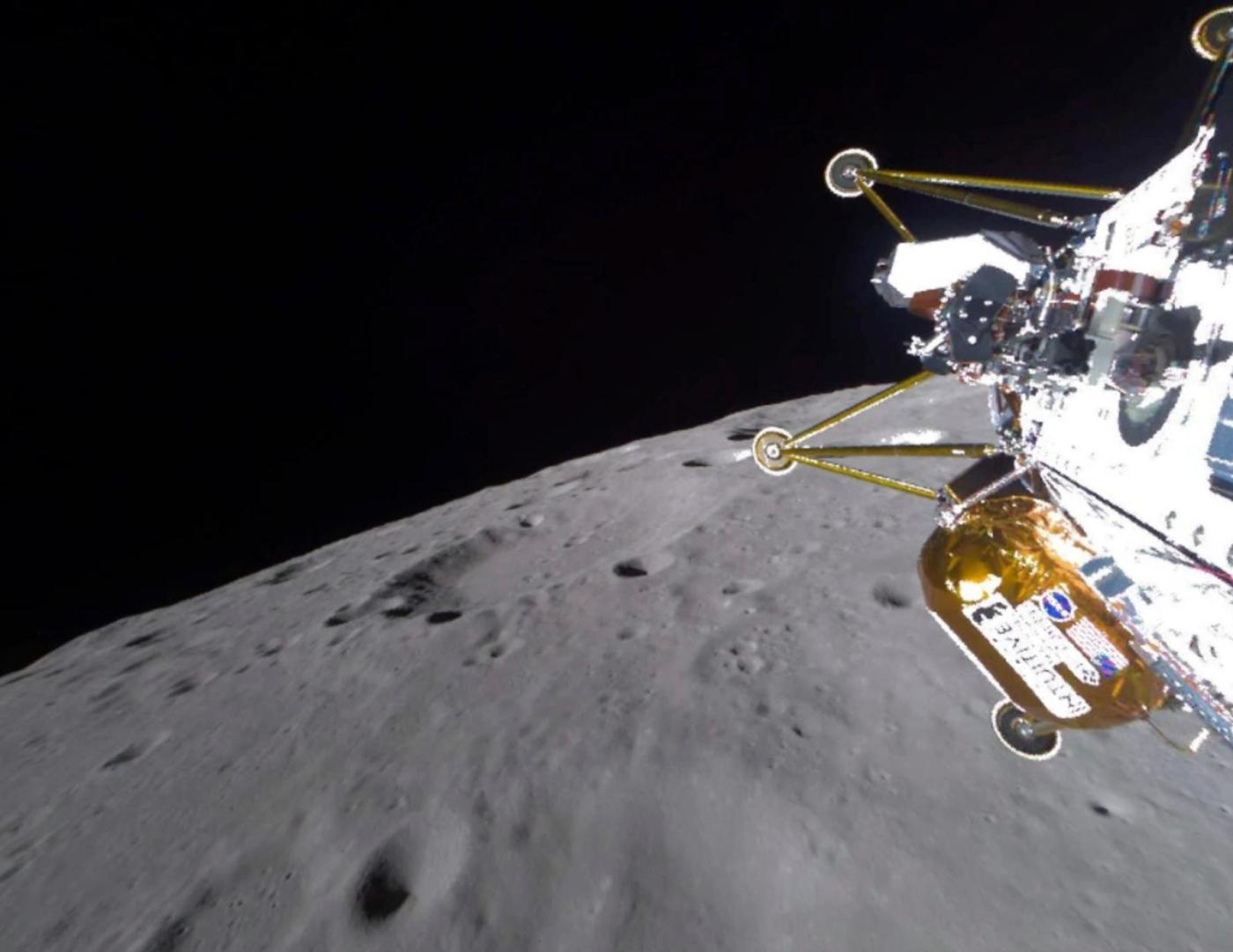
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — A private lunar lander is no longer working after landing sideways in a crater near the moon’s south pole, officials said Friday.
Related Articles
SpaceX’s latest Starship test flight ends with another explosion
After 9 months stranded in space, 2 NASA astronauts nearing their return to Earth
Asteroid 2024 YR4 is no longer a threat to Earth, scientists say
SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base visible in Santa Cruz
Telescopes spy a monster radio jet streaming from a bright and early object in the universe
The botched landing attempt ended the mission by Texas-based Intuitive Machines.
Launched last week, the lander Athena missed its mark by more than 800 feet, the company said in declaring it dead.
Athena managed to send back pictures confirming its position and activate a few experiments before going silent. NASA and other customers had packed the lander with tens of millions of dollars’ worth of experiments including an ice drill, drone and pair of rovers to roam the unexplored terrain ahead of astronauts’ planned arrival later this decade.
It’s unlikely Athena’s batteries can be recharged given the way the lander’s solar panels are pointed and the extreme cold in the crater.
“The mission has concluded and teams are continuing to assess the data collected throughout the mission,” the company said in a statement.
This was the second landing attempt for Intuitive Machines. The first, a year ago, also ended with a sideways landing, but the company was able to keep the lander going for longer than this time. Despite all the problems, the company’s first lander managed to put the U.S. back on the moon for the first time in more than 50 years.
Earlier in the week, another Texas company scored a successful landing under NASA’s commercial lunar delivery program, intended to jumpstart business on the moon while preparing for astronauts’ return. Firefly Aerospace put its Blue Ghost lander down in the far northern latitudes of the moon’s near side.
Firefly CEO Jason Kim reported Friday that eight of the 10 NASA experiments on Blue Ghost already have met their mission objectives. It’s expected to operate for another week until lunar daytime ends and solar power is no longer available.
The south polar region of the moon is particularly difficult to reach and operate on given the harsh sun angles, limited communications with Earth and uncharted, rugged terrain. Athena’s landing was the closest a spacecraft has come to the south pole, just 100 miles away.
That’s where NASA is targeting for its first landing by astronauts since the 1960s and 1970s Apollo program, no earlier than 2027. The craters are believed to hold tons of frozen water that could be used by future crews to drink and turn into rocket fuel.
Intuitive Machines has contracts with NASA for two more moon landing deliveries. The company said it will need to determine exactly what went wrong this time before launching the next mission. After the 15-foot Athena landed, controllers rushed to turn off some of the lander’s equipment to conserve power while trying to salvage what they could.
In both landings by Intuitive Machines, problems arose at the last minute with the prime laser navigation system.
Intuitive Machines’ rocket-propelled drone, Grace, was supposed to hop across the lunar surface before jumping into a crater to look for frozen water. The two rovers from two other companies, one American and one Japanese, were going to scout around the area as well.
NASA’s ice drill experiment was activated before the lander’s batteries died. How much could be accomplished was not immediately known. Several other objectives were accelerated and milestones met, according to the company.
NASA paid $62 million to Intuitive Machines to get its three experiments to the moon.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.